Chassis Layout of Automobile
Chassis Layout of Automobile
The chassis frame is a basic framework of the automobile. This frame supports all the parts of the automobile attached to it. This frame is made of a material like drop-forged steel. All the parts of the automobile are attached to it only. All the systems related to automobile-like power plant, transmission, steering, suspension, braking system etc. are supported by chassis frame only.
Don't Miss:
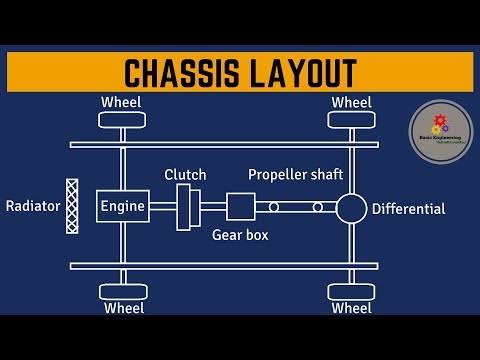
Chassis Layout –
Description of chassis layout as below:
A) Chassis Frame – It supports the engine, wheels, steering, body, braking system, suspension assembly.
B) Radiator – Radiators are used for cooling internal combustion engines. For that purpose, the radiator is placed at the very front of the engine of the automobile.
C) Engine – It is the power source of the automobile, from which power is to be generated to drive the automobile.
D) Clutch – A clutch is a mechanical device which engages & disengages power transmission especially from driving shaft to driven shaft.
E) Gearbox – A gearbox is a system that uses integrated gears with a specific arrangement to transmit the power.
F) Universal Joint – A universal joint is a joint or coupling connecting rigid rods whose axes inclined to each other.
G) Propeller Shaft – Propeller shaft is a mechanical component used for transmitting torque & rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drive train that cannot be connected directly that need to allow for relative movement between them.
H) Differential – A differential is a gear train with three shafts that has the property of the rotational speed of one shaft is the average of the speeds of others.
Types of Chassis Layout
According to the arrangement of engine & transmission the following types of layout are given as :
1. Front Engine Front Wheel Drive
In this layout, both the internal combustion engine and driven road wheels at the front of the vehicle.
2. Front Engine Rear Wheel Drive
In this layout, internal combustion engine placed at front and driven road wheels located at the rear of the vehicle.
3. Mid Engine Rear Wheel Drive
In this layout, the engine is between or behind the rear wheels & drives the front wheel via a driven shaft.
4. Rear Engine Rear Wheel Drive
In this layout, both the engine and drive wheels located at the rear of the vehicle.
5. All Wheel Drive
In this layout, a two-axled vehicle drive train capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand & its typically linked via a transfer case providing an additional output drive shaft and in many instances, additional gear ranges.
Don't Miss:









0 comments:
Post a Comment